Piles Treatment in Singapore
Piles are a very common problem in Asia. Piles are an abnormal swelling of blood vessels in the anus. Sometimes, these swellings can enlarge gradually to become a big lump at the anus. At other times, these blood vessels swelling can burst and result in passage of fresh blood from the anus after defecation.
What are the Symptoms of Piles?
- Bleeding from the rectum
- Lump in the anal region
- Anal itch
- Anal pain
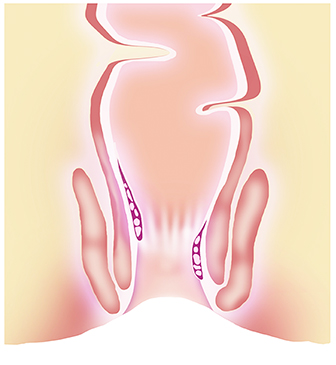
What are the Various Grades of Piles?
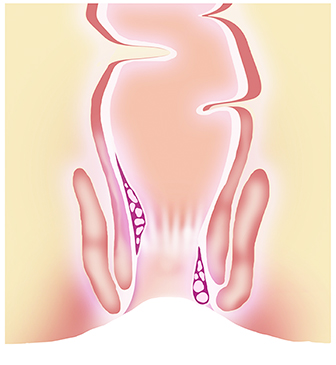
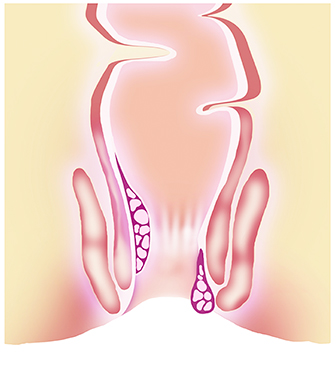
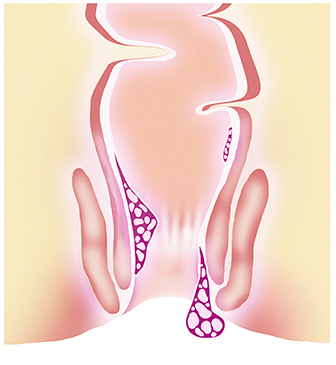

What are the Piles Treatment Options?
- Medications
- Rubberband Ligation
- Injection Sclerotherapy
- Traditional Haemorrhoids Surgery (Haemorrhoidectomy)
- THD (Transanal Haemorrhoidal Dearterisation)
- Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy
THD (Transanal Haemorrhoidal Dearterisation)
Many modalities have been used for first- and second-degree piles treatment, including medications, rubber ligation and sclerotherapy. Surgical excision is performed if non-surgical options failed to address the problem. A newer technique of Transanal Haemorrhoidal Dearterisation (THD) has gained popularity in the treatment of early stages of piles over the past 5 years. This technique involved the ligation of the distal branches of the superior rectal artery and thus drastically reducing blood supply to the haemorrhoidal plexus. This in turn reduces the haemorrhoidal congestion with the result of decrease haemorrhoidal bleeding and prolapse. The use of a transanal vascular Doppler allows precise ligation of the haemorrhoidal vessels at or above the level of the anorectal junction. Unlike rubberband ligation of piles, this procedure does not produce the distressing sensation of tenesmus. It is relatively painless procedure as the ligation of vessel is proximal to the dentate line and transitional epithelium of the anal canal. A haemorrhoidopexy can also be performed if there is a small component of hemorrhoidal prolapse. Many studies have shown that THD is a very effective procedure for the treatment of first- and second-degree piles. THD is less effective for third degree piles, especially if the predominant symptom is prolapsed and not bleeding. However, THD can still be offered to patients with third degree piles and refused excisional haemorrhoidectomy.
Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy
Severe cases of 3rd and 4th degree pile will require haemorrhoids surgery by your Singapore piles surgeon. Traditional piles surgery is notorious for the high level of pain because of the large open wound after surgery. However, newer technique of stapled haemorrhoidectomy has greatly reduced the pain after piles surgery.
This surgical technique has become increasing popular over the past ten years. To date, many large international trials have shown that randomized controlled a clear advantage of stapled haemorrhoidectomy compared to conventional piles surgery. The complication rate of this new procedure is also comparable to that of conventional methods.
- KH Ng et al. Experience of 3711 stapled haemorrhoidectomy operations. British Journal of Surgery. 2006 Feb.
- KH Ng et al. Modified Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy: A suggested improved technique. Australian New Zealand Journal of Surgery. May 2008.
Benefits of Stapled Haemorrhoidectomy
- Less pain
- Faster recovery
- Faster return to work and daily activity